【World Allergy Week 2024】Overcoming barriers to preventing and treating food allergies

Food allergies are becoming more common in people of all ages around the world, and this is a global health problem.
World Allergy Week 2024
Overcoming barriers to preventing and treating food allergies

Food allergies can be life-threatening
Food allergies can be life threatening. Immediate treatment with epinephrine during anaphylaxis is critical. Preventing severe reactions is possible with awareness and the right treatment. Obtaining a correct diagnosis by a physician with allergy expertise is critically important to avoid missing cases or over diagnosis.
What is food allergy
Food allergy refers to the adverse health effects caused by a specific immune response when exposed to a specific food. It can also be defined as a harmful immune response caused by food. This reaction can be harmful to the human body when exposed to a specific food repeatedly. According to its mechanism, food allergy can be divided into IgE-mediated, non-IgE-mediated and mixed mechanism-mediated [1].
IgE-mediated food allergy: usually occurs rapidly after exposure to food, often causing urticaria/angioedema, oral allergy syndrome (pollen-food allergy syndrome), rhinitis, asthma, immediate gastrointestinal hypersensitivity Reactions/Gastrointestinal Symptoms, Severe Anaphylaxis, Delayed Food Anaphylaxis to Mammalian Meats, Food-Related Exercise-Induced Severe Anaphylaxis, etc.
Non-IGE-mediated food allergy: Reactions generally occur more than 1-2 hours after eating, and the reactions are mostly gastrointestinal symptoms. It can cause food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome, food protein-induced allergic proctitis, celiac disease (gluten-sensitive enteropathy), etc.
Mixed-mediated food allergy: common ones include atopic dermatitis, eosinophilic gastroenteritis, etc.
What are the symptoms of food allergies?
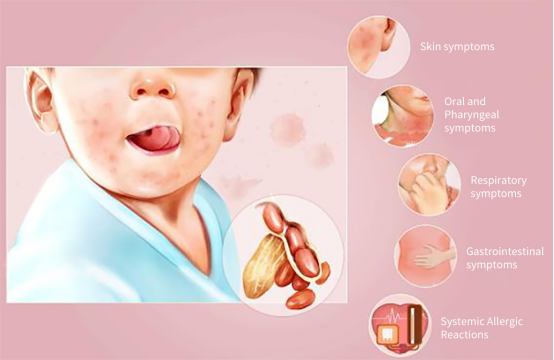
Food allergies often involve different organs, causing patients to experience symptoms in the skin, mucous membranes, respiratory tract, circulatory system, digestive system, and nervous system (Table 1).
Common symptoms of food allergies (Table 1)
disease name | common food allergens |
IgE-mediated allergic reaction | |
Immediate IgE-mediated allergic reaction | Any food is possible. Common allergenic foods in infants and young children around the world are milk and eggs. In North America and European countries, they are often peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, and fish. In Asian countries, wheat and buckwheat are more common. |
a-galactofusion IgE-mediated anaphylaxis | Mammalian meat, such as beef, pork, mutton, etc. Some baby also react to mammalian milk and dairy products |
Food-related exercise-induced severe allergic reactions | The most common are wheat, shellfish, and celery |
oral allergy syndrome | Raw fruits, vegetables, nuts, etc. Tolerated if food is cooked |
Non-IgE-mediated allergic reactions | |
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome | Milk, soybeans, rice, oats |
Food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis | Mothers of breastfeeding infants ingesting milk, soy, and/or eggs; formula feeding |
Celiac disease | Gluten, such as wheat, rye, barley |
mixed mediated food allergic reactions | |
atopic dermatitis | Common food allergens, especially milk and eggs |
eosinophilic gastroenteritis | variety of food |
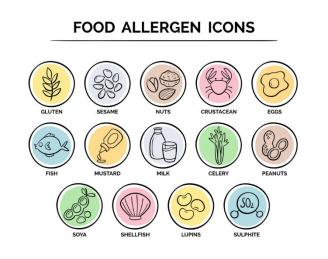
Common food allergens (Table 2)
The most common food allergens include milk, eggs, soybeans, wheat, peanuts, fish, shrimp, nuts, etc. 90% of food allergies are caused by these eight types of food [2].
Dangers of food allergies
Food allergies usually affect patients' quality of life. Patients with allergies may develop related allergic symptoms after eating specific foods: oral allergy symptoms such as oropharyngeal itching, lip/oral mucosal edema; skin symptoms such as rash, skin itching; digestion Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc. In addition, food allergies can also induce severe allergic reactions and even anaphylactic shock, which can endanger the patient's life.
How are allergic diseases properly managed and treated?
The principles of allergic disease treatment recommended by WHO: Combination of prevention and treatment, four-in-one
environmental control, drug treatment, health education, desensitization treatment.


1. Evidence based Guidelines for Food Allergy in Chinese Children (2022 Edition)
2. Ansotegui IJ, Melioli G, Canonica GW, et al. IgE allergy diagnostics and other relevant tests in allergy, a world allergy organization position paper. World Allergy Organ J, 2020, 13(2): 100080. DOI: 10.1016/j.waojou.2019.100080